PVTIME – On 5 December 2024, the China Photovoltaic Industry Association (CPIA) held its annual conference in Sichuan, China. At the conference, Wang Bohua, Honorary Chairman of CPIA, presented a comprehensive review of the photovoltaic industry in 2024 and provided CPIA’s outlook on the development of the photovoltaic industry in 2025.

Mr. Wang Bohua commenced his presentation by outlining the remarkable accomplishments of China’s PV industry in 2024. He emphasised that Chinese PV companies had made considerable headway in terms of trade, technology and industry performance, both in the domestic market and overseas.
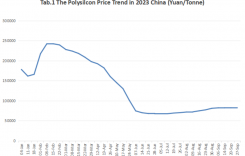
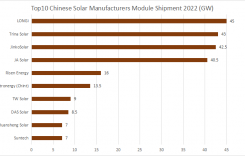
The latest figures show that China added 181.3GW of new PV capacity between January and October 2024, representing a year-on-year increase of 27.3%. Meanwhile, output of key materials such as polycrystalline materials, wafers, solar cells and modules reached 1,580,000MT, 608GW, 510GW and 453GW respectively during the same period, representing year-on-year growth of more than 20%.
During the reporting period, there was a year-on-year increase of 41.8% and 15.9% respectively in the export volume of solar cells and modules. The total export value of wafers, cells and modules is estimated to be 28.14 billion dollars, representing a year-on-year decrease of 34.5%. India, Turkey and Cambodia represent the top three export markets for solar cells. Europe represents the largest solar module export market, although there has been a notable decline in market share. In addition to Europe, there has been a notable increase in market share in South Asia, Latin America and the Middle East. The solar cell export market has become increasingly diversified, with more than a third of the market situated outside the top ten, comprising numerous emerging markets.
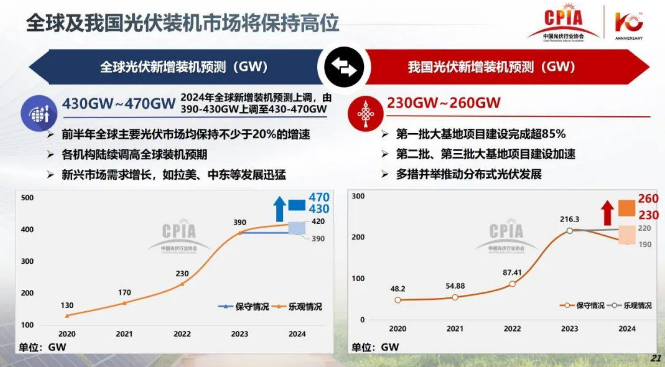
The global PV market is estimated to grow by more than 20% in the first half of 2024. Most institutions have revised their renewable energy installation targets upwards, from 390-430GW to 430-470GW for 2024. China, the leading PV producer, is estimated to have 230-260GW of newly planned solar installations. According to the IEA, between 500GW and 700GW of solar PV will need to be installed between 2024 and 2030 to tackle the climate issues.
By 2025, construction of the first batch of large commercial and industrial solar plants in China will be 85% complete, while the construction of the second and third batches of PV projects will be accelerated.
Additionally, a number of initiatives will be implemented to drive distributed PV development in China, as well as PV plants for sand control, offshore PV, and new technologies.
Furthermore, the China Energy Law was approved on 8 November and will be enacted on 1 January 2025. By then, the entire society will give priority to clean energy sources such as photovoltaic. The construction of clean energy transport infrastructure and the rapid development of new buildings utilising clean energy are also planned. To advance photovoltaic technology, it is essential to align its development with market demand to enhance power yields, minimise carbon footprints and customise solutions to market requirements.

Scan the QR code to follow PVTIME official account on Wechat for latest news on PV+ES