PVTIME – As the global energy transition accelerates, the photovoltaic (PV) industry, as a key force in the renewable energy sector, has always been in the spotlight. On 27 February, at the PV Industry Development Review for 2024 and Outlook for 2025 seminar hosted by the China Photovoltaic Industry Association (CPIA). Mr Wang Bohua, Honorary Chairman of the Association, comprehensively reviewed the development of the PV industry in China in 2024 and made important predictions about its development in the coming year, providing valuable guidance to industry participants.
Global PV industry boomed in 2024, with China’s market facing opportunities and challenges
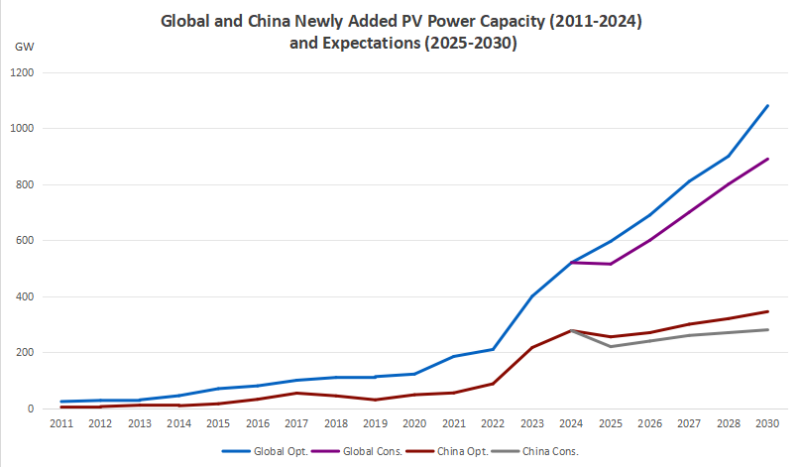
In 2024, the global PV industry entered a golden period of rapid development. The global newly installed PV capacity increased by approximately 35.9% year on year, and all major global PV markets maintained a growth rate of no less than 15%. This achievement shows that PV energy is becoming more and more important in the global energy structure and has gained wide recognition and active application worldwide.
As a major player in the global PV industry, China’s performance in 2024 was remarkable. China’s newly installed PV capacity reached 277.57GW in that year, with a year-on-year growth rate of 28.3%. Although the growth rate was slightly lower than the global average, China still held a pivotal position in the global PV market.
China’s PV manufacturing industry demonstrated its strong capabilities in 2024. The production of polysilicon, wafers, cells and modules reached 2.43 million tonnes, 5450GW, 4850GW and 4200GW respectively, with year-on-year growth rates of 37.8%, 35.8%, 36.1% and 35.5%. Such substantial production growth not only consolidated China’s leading position in the global PV industry, but also highlighted its strong production capacity and market competitiveness.
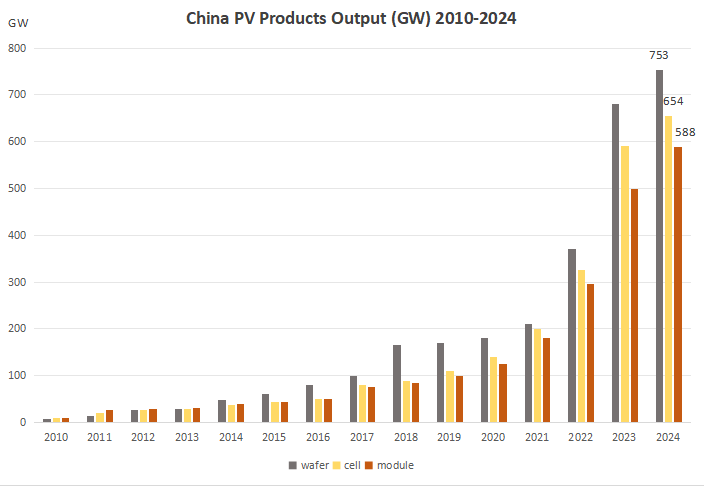
Source: CPIA
Although the export volume of PV products continued to grow, with the export volume of wafers, cells and modules increasing by 34.7%, 30.4% and 18.3% respectively year-on-year, the export value decreased. The export value of wafers, cells and modules decreased by 31.8%, 24.5% and 24.7% respectively year-on-year. The main reason for this phenomenon was the significant drop in PV product prices. The increase in export volume could not offset the losses caused by the price decline.
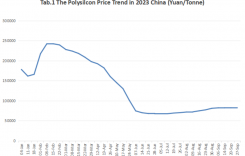
Looking at the price trend, from January to November 2024, the prices of polysilicon, wafers, cells and modules fell by more than 35%, 45% and 25% respectively. The sharp drop in prices had a significant impact on the output value of the PV manufacturing sector. In 2024, the output value of China’s PV manufacturing sector (excluding inverters) was approximately 1.2 trillion yuan, down 32.4% year-on-year, resulting in most sectors operating at a loss in the second half of 2024. These data indicate that China’s PV industry urgently needs to strengthen cooperation in capacity planning, policy support, technological innovation and exploration of new application scenarios to achieve healthier and more sustainable development.
2025: Uncertainties and opportunities coexist in China’s PV market
Regarding the development of China’s PV market in 2025, Mr Wang Bohua predicted that China’s newly installed PV capacity will reach 215 to 255GW. Compared with 2024, it could decrease by 8.13% to 22.54% year-on-year. This prediction attracted widespread attention in the industry, and the main reason for this potential decline was closely related to policy factors.
In 2025, policies such as the distributed PV power generation management measures and the market-based reform of new energy on – grid electricity prices were introduced. Due to the time lag between the introduction of these policies and the specific implementation measures of various provinces, there was a degree of “wait and see” sentiment in the industry, which increased the uncertainty of the 2025 installed capacity forecast. In addition, issues such as power consumption and integration have constrained the industry’s development, and the industry has fully anticipated the slowdown in the growth rate of newly installed capacity.
Different PV markets have different development trends. The residential PV market is expected to remain weak in 2025 due to insufficient grid capacity and reduced economic viability. In contrast, the industrial and commercial PV market is expected to continue to grow, driven by the shift from dual control of energy consumption to dual control of carbon emissions and the increase in industrial electricity prices. Demand for centralised PV capacity over the next two years will focus on large-scale wind and solar base-load projects. In the long term, it is still necessary to wait for the completion of the construction of ultra-high voltage transmission lines to effectively break the bottleneck of power consumption and integration.
Although China’s newly installed PV capacity may decline, it should be noted that the fundamental drivers of market growth remain strong. On the one hand, China has accumulated strong capabilities in PV technology R&D and industrial manufacturing. On the other hand, domestic demand for clean energy remains high and relevant policies continue to promote the healthy development of the PV industry. Therefore, although China’s PV market faces challenges, it still has many opportunities in 2025.
2025: Global PV market continues to grow
In 2025, global installed PV capacity will continue to grow. Optimistically, global newly installed PV capacity is expected to grow by 10% year on year. The report by TrendForce’s New Energy Research Center, an independent market institution, shows that global newly installed PV capacity will reach 596 GW in 2025, with a year-on-year growth rate of 6.0%. Although the growth rate is slower than before, given that the PV industry has entered a mature stage of development, this growth rate still demonstrates strong market potential and industry resilience.
From a regional market perspective, China, Europe and the United States remain the main growth markets for global PV. However, due to the high base effect, their growth rates are gradually slowing and their share of installed capacity is also declining. In contrast, regions other than China, Europe and the United States are experiencing rapid growth in PV demand, driven by factors such as rigid electricity demand, urgent energy transition needs and energy policy goals, and their share of installed capacity is steadily increasing.
Source: CPIA
In 2025, newly installed PV capacity in Asia-Pacific is expected to reach 364.3 GW, an increase of 4.0% year-on-year. China and India play a leading role in this region. The Southeast Asia region shows a high growth trend in installed PV capacity due to its energy transition needs and growing industrial electricity demand. In the Americas, newly installed PV capacity is expected to reach 92.8 GW, an increase of 15.4% year-on-year. The increase in installed capacity is still mainly dependent on the United States, but Brazil’s growth rate has slowed and its share has declined. Grid connection and consumption issues, as well as financial pressures in the Latin American regions, have become the main obstacles to the future development of the PV industry in the Americas. Newly installed PV capacity in Europe is expected to reach 101.5 GW in 2025, with an annual growth rate of 6.2%. Germany, Spain and the Netherlands are the top three countries in terms of installed capacity. Although Europe faces challenges such as low electricity demand and often negative electricity prices, driven by long-term renewable energy and coal phase-out targets, demand for installed PV capacity remains strong. In 2025, newly installed PV capacity in the Middle East and Africa market will reach 37.5 GW, with an annual growth rate of around 3.3%. Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and South Africa will be the main contributors to installed capacity demand. Emerging incremental markets such as Egypt and Oman remain to be developed. In recent years, private PPA projects, with their relatively high market-based electricity prices, have gradually become active in the Middle East and Africa market as PV module prices have continued to fall.
Industry Development: Positive Factors Inject Sustained Momentum into the PV Industry
Although the PV industry faces challenges such as a slowing growth rate, it also has many positive factors that provide strong momentum for the sustainable development of the industry.
From a policy perspective, governments around the world have introduced policies to support the development of the PV industry. China is guiding market adjustments through policy, promoting research, development and application of high-efficiency battery technologies, and helping companies overcome trade barriers by building factories overseas and acquiring local companies. The US Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technology Office (SETO) is launching an annual funding programme to provide direct financial support for PV research, development and demonstration projects. The German Ministry of Economics has proposed a new draft law with the aim of achieving “100% renewable energy supply and phasing out fossil fuels” by 2035. The introduction of these measures has created a favourable policy environment for the development of the PV industry.
Technological advances in PV technology and continuous optimisation of production costs have made PV power generation the most cost-effective energy solution in more and more regions. Especially in areas with abundant sunlight resources, the price of PV electricity is already lower than that of traditional thermal power. This has encouraged more and more enterprises and users to install PV power generation equipment, which has greatly promoted the rapid growth of global PV installed capacity. Many PV enterprises have achieved remarkable results in technological innovation. The PV Technology Center of Tongwei Co., Ltd. announced a breakthrough in the performance and conversion efficiency of high-efficiency heterojunction modules. JA Solar exhibited the DeepBlue5.0 ultra-high performance module. LONGi the PV giant launched the Hi-MO X10 distributed module product based on HPBC2.0 battery technology. These technological innovations and product iterations will further reduce the cost of PV power generation and accelerate the popularisation and application of PV energy.
The rise of emerging markets has also brought new development opportunities to the PV industry. Regions such as the Middle East and Africa are rich in sunlight resources, providing unique natural conditions for the development of the PV industry. With the gradual improvement of power grid infrastructure and the further establishment of market-based mechanisms in these regions, the growth rate of PV installed capacity is expected to continue to increase, injecting new vitality into the diversified development of the global PV market. For example, the Middle East region, with its rich solar energy resources and proactive policy support, has become a new driving force for the growth of the global PV market.
Conclusion and Outlook
Mr Wang Bohua’s comprehensive review of the development of the PV industry in 2024 and accurate outlook for 2025 provide important decision-making references for practitioners in the PV industry. Although China’s newly installed PV capacity may decline in 2025, there is still plenty of room for growth in the global PV market.
It is necessary for Chinese PV companies to actively respond to challenges and seize opportunities. In terms of capacity planning, it is necessary to be more scientific and rational to avoid blind expansion. In terms of technological innovation, continuous investment should be made to enhance product competitiveness. In terms of market expansion, while consolidating the domestic market, it is also necessary to actively expand overseas, especially in emerging markets. At the same time, enterprises should strengthen upstream-downward cooperation to create synergy for development.
From a global perspective, countries should strengthen technical exchanges and cooperation in the PV field to jointly address issues such as insufficient grid capacity and the consumption and integration of wind and solar power. Through policy coordination and technology sharing, the global PV industry can be encouraged to develop in a healthier and more sustainable direction. It is believed that by jointly promoting policy support, technological progress and market demand, the PV industry will play a greater role in the global energy transition and contribute significantly to the global goal of carbon neutrality.

Scan the QR code to follow PVTIME official account on Wechat for latest news on PV+ES